Military Training: How The World’s Top 5 Elite Forces Train
Bodybuilding, while not the primary focus of military training, can still play a significant role in enhancing the performance of soldiers.
Check Out: Olympic Lifting : 25 Strategies That Work
Here are several reasons why bodybuilding can be important in the military context:
Physical Preparedness
Bodybuilding helps soldiers develop strength, endurance, and overall physical fitness, which are essential for carrying heavy loads, navigating difficult terrain, and engaging in combat situations. A well-developed physique can improve a soldier's ability to perform a wide range of tasks efficiently.
Injury Prevention
Strengthening muscles and improving joint stability through bodybuilding exercises can help reduce the risk of injuries, particularly during physically demanding activities like carrying heavy gear, running, and jumping. Strong muscles and joints provide better support and protection, decreasing the likelihood of strains, sprains, and other injuries.
Functional Strength Military Training
Bodybuilding exercises often focus on compound movements that mimic real-world actions. Soldiers need functional strength to perform tasks such as lifting, carrying, climbing, and pushing/pulling objects in various situations encountered in combat or during training exercises.
Mental Resilience
Bodybuilding requires discipline, dedication, and mental toughness to stick to a structured training program and push through physical discomfort. These mental attributes are also crucial in the military, where soldiers must endure challenging conditions, maintain focus under stress, and persevere in demanding situations.
Confidence and Morale
Building a strong, muscular physique can boost a soldier's confidence and self-esteem, which can translate into improved performance and morale. Feeling physically capable and confident in one's abilities can positively impact a soldier's mindset on the battlefield and during training exercises.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Injured soldiers often undergo rehabilitation programs that include strength training to regain mobility, stability, and strength in injured areas. Bodybuilding exercises tailored to specific rehabilitation needs can accelerate recovery and help soldiers return to duty faster.
Improved Endurance
Bodybuilding routines that incorporate high-repetition sets and cardiovascular exercises can enhance soldiers' endurance levels, allowing them to sustain physical exertion for longer periods without fatigue. This endurance is crucial during prolonged missions, marches, or engagements.
Enhanced Metabolic Health
Regular resistance training and muscle-building exercises can improve metabolic health by increasing muscle mass, reducing body fat, and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Soldiers with better metabolic health are less prone to obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders, which can impact operational readiness.
Resilience to Environmental Stressors
Building muscle through resistance training can help soldiers better tolerate extreme environmental conditions, such as heat, cold, altitude, and humidity. Increased muscle mass provides insulation and helps regulate body temperature, while improved cardiovascular fitness supports efficient oxygen delivery to tissues.
Functional Movement Patterns
Bodybuilding exercises often focus on compound movements that involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together. These functional movement patterns translate directly to the dynamic and varied physical demands faced by soldiers in combat and operational environments.
Enhanced Physical Agility
Bodybuilding can improve agility, coordination, and proprioception, which are essential for navigating obstacles, evading threats, and reacting quickly to changing situations. Agility training can help soldiers move more efficiently and effectively in urban, jungle, mountainous, or other challenging terrain.
Optimized Body Composition
Bodybuilding promotes the development of lean muscle mass while reducing excess body fat, leading to an optimized body composition. Soldiers with a higher muscle-to-fat ratio tend to perform better in physical tasks, have higher strength-to-weight ratios, and experience fewer mobility limitations.
Combatting Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, can impact older soldiers' performance and resilience. Bodybuilding exercises can mitigate sarcopenia by stimulating muscle protein synthesis, preserving muscle mass, and maintaining functional strength as soldiers age.
Improved Resilience to Blast Injuries
Strengthening muscles, tendons, and ligaments through bodybuilding can provide added protection and resilience against blast injuries, which are common in modern combat environments. A stronger musculoskeletal system can help soldiers withstand the physical impact of explosions and reduce the severity of injuries.
Promotion of Camaraderie and Team Cohesion
Group workouts and training sessions focused on bodybuilding can foster camaraderie, teamwork, and mutual support among soldiers. Shared goals, challenges, and successes in the gym can strengthen unit cohesion and morale, leading to more effective collaboration in operational settings.
Positive Influence on Mental Health
Engaging in regular bodybuilding activities can have positive effects on soldiers' mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and depression levels. Physical exercise stimulates the release of endorphins and other neurotransmitters associated with improved mood and cognitive function, which can benefit soldiers both on and off the battlefield.
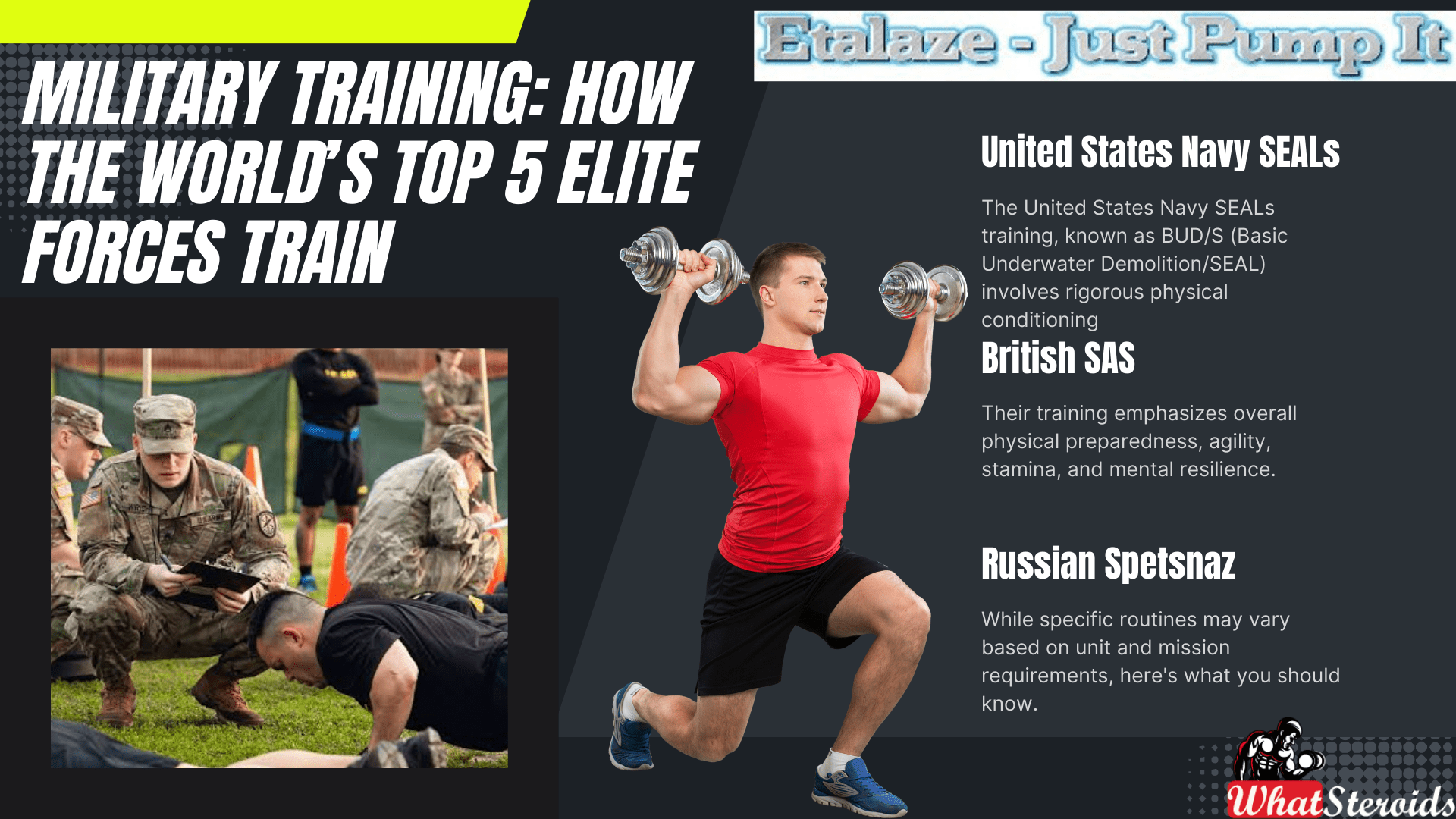
United States Navy SEALs (USA)
The United States Navy SEALs training, known as BUD/S (Basic Underwater Demolition/SEAL) involves rigorous physical conditioning, including:
Running and Swimming
Long-distance running and swimming are core components of SEAL training to build endurance and cardiovascular fitness.
Calisthenics
Bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, sit-ups, and squats are done in high repetitions to build strength and endurance.
Weight Training
SEAL candidates incorporate weightlifting to build muscular strength and power. This includes exercises like deadlifts, squats, bench presses, and overhead presses.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
SEALs train with high-intensity interval workouts to improve anaerobic endurance and overall fitness.
Obstacle Courses
SEAL candidates navigate through challenging obstacle courses to improve agility, coordination, and mental toughness.
Combat Conditioning
Military training drills simulate combat situations, emphasizing functional movements and combat-related skills.
Flexibility Training
Stretching and mobility exercises are incorporated to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries.
Water Confidence Training
Extensive swimming drills are conducted, including underwater swims, to enhance comfort and confidence in aquatic environments.
Overall, the training routine is designed to push candidates to their physical and mental limits, preparing them for the demanding tasks they'll face as Navy SEALs.
Must Read: What is EPO and Blood Doping in Cycling and Endurance Sports?
British SAS (United Kingdom)
Obstacle Course Training
Circuit Training
Rucking
Combat Conditioning
Endurance Military Running
Israel Special Forces (Israel)
Warm-up
Compound Exercises
Recent Posts
Creatine vs Myostatin: An Expert’s Analysis
Myostatin, a protein encoded by the MSTN gene, acts as a regulator of muscle growth.…
Raloxifene (Evista) 101: A Non-Surgical Solution for Gyno
Raloxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), is one of the most valuable yet less…
Mastering Bodybuilding in 2025: Top Fitness Tips for Success
Bodybuilding is more than just a sport; it's a lifestyle that requires dedication, discipline, and…
Why Post-Cycle Therapy (PCT) Fails After a Nandrolone Cycle
Nandrolone, or Deca Durabolin, is an injectable anabolic steroid often used by bodybuilders during the…
Counteracting Anabolic Resistance with Adaptogens in Aging Men
As people age, maintaining muscle mass and strength becomes increasingly challenging due to a natural…
Tips on How to Store Peptides and HGH
When peptides are mixed with bacteriostatic water (BAC water), their longevity is highly influenced by…



